Before I read a recommended book, I may go to watch or read book summaries first, especially if I am unfamiliar with the author. This will give me an overview of the content before I decide to dive deeper into the book. This is what I have learnt from this good summary by YouTuber "The Swedish Investor".
Beating the Street by Peter Lynch
By the Swedish Investor
Compiled on 8th Aug 2021
Youtube link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ihsCWCiJozQ
5 Key takeaway from the book:
1. Focus on the “EVEN BIGGER PICTURE”
Price in the stock market is determined by emotional human beings. Thus stocks go through cycles, and swings caused by market sentiments.
“Key to making money is not to get scared out of them” – Peter Lynch. Thus, the stomach determines the outcome of the stock pick, not the head. When Lynch feels the itch to sell the stocks, he reminds himself about the even bigger picture. From 1959 to 2018, stocks outperformed bonds (7.1% stocks per annum versus 2.1% bonds per annum after inflation). This is over 3x. Bonds refer to the 10-year treasury.
If a disaster happens, money in the bank is just as useless. Thus, in the longer run, the stock picker should be a winner.
2. Making money in stocks is a combination of science, art and legwork
Science
As per the figures presented in the company’s financial statement. Some of the items that Peter Lynch pays attention to:
Growing sales and earnings
Reasonable price
Low debt, and
Buyback of shares
Art
Need to know what caused the sales and earnings to grow in the past and also what may lead to growth in the future.
You need to be able to explain the business in simple language that a fifth-grader could understand without getting bored (quickly).
Legwork
Stay busy. Peter Lynch visited hundreds of companies per year, read reports and spoke to the managers. From a visit to every 10 companies, you should find one that is better than what the market is expressing (ie undervalued). When you investigate an opportunity, you usually stumble upon another.
Favourite Question to CEO: “Are there any other companies that you are impressed with?”. If one spoke fondly of a competitor, you have probably found a good deal.
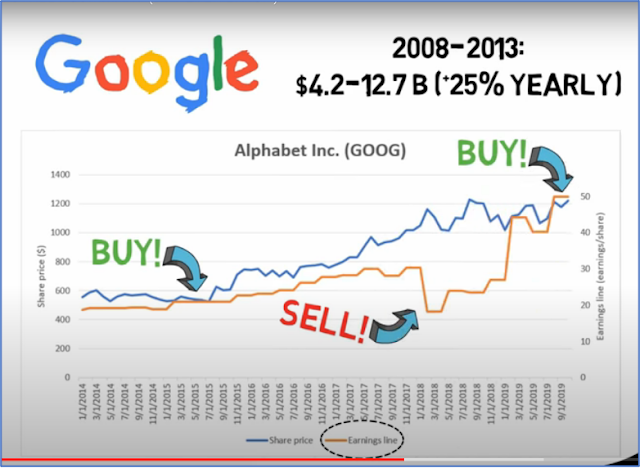
3. Use the “earnings line” to identify buying opportunity
2 areas to look into:
Sales and earnings increase
Buy at a reasonable price
The price of a stock will eventually follow the curve of the earnings. Thus, if earnings are moving slower than the share price, there is room for the price to catch up with the earnings.
Eg given of GOOGLE whose earnings went from $4.2 to $12.7B between 2008 to 2013 (which is a 25% annual growth). If we believe that Google can continue such a growth rate.
Rule of thumb: Stocks should sell at P/E below the yearly growth rate. Thus, when google P/E drops below 25 (using the Google example of 25% annual growth), it is considered a buy.
4. Search overlooked stocks with strong owners
It pays to be contrarian coming to investing. It can be very profitable to go to places where fund managers do not visit and not followed by analysts.
Eg. Principle #18 – when even the analysts are bored, it is time to start selling. Founders still typically own large proportions of shares.
Strong owners are the ones who have succeeded before but the institutional players probably do not know or care. These institutional players rarely know much about the industry.
5. Look for great companies in lousy industries
Look for stocks with (10) traits of a ten-bagger.
Where would you rather invest your money today if given the choices below:
Strong performance attracts attention and competition. As competition falls, profits go up and it would not take long before price follows to go up.




Comments
Post a Comment